
Asset Management Manual
A guide for practitioners!

Asset Management Manual
A guide for practitioners!
YULI PAN & JUNZHE WANG, National Engineering Research Center of Road Maintenance Technologies, PR China
This case study describes the annual based asset management carried out by Jiangsu Provincial Highway Administration Bureau for their trunk highways since 2008, as plotted in Figure 4.1.6.3, its scale increases 1.7 times within a period of 10 years.
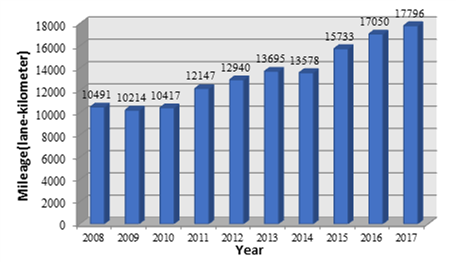
Figure 4.1.6.3: Scale of the Asset Management of Jiangsu Province
The main purpose of the annual application of asset management in Jiangsu province is to enhance the highway network management skills by using modern asset management equipment and systems, including high-speed highway condition monitoring vehicles, database and decision-making systems (L, Gao and X, Zhang. 2017).
Through the implementation of this asset management program, the Highway Administration Bureau is benefited in several ways:
The annual based asset management is conducted stage by stage as follows:data collection → distress auto-recognition → maintenance analysis → planning, scheduling and presentation.
Data Collection
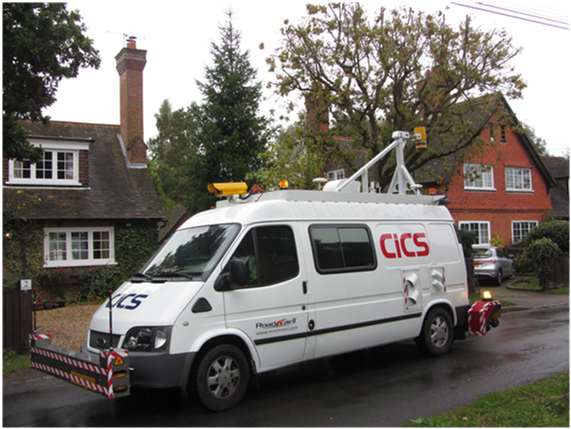
Figure 4.1.6.4 is one of the three high-speed highway condition monitoring vehicles (CiCS: China's highway information Collection System) employed in Jiangsu's trunk highway investigations. The CiCS vehicle is able to collect highway conditions including cracking, pot hole, longitudinal profiles, transverse profiles, pavement texture, grade, curvature, and slope, front images, and GPS etc. information all together with traffic stream speeds.

Distress Auto-recognition
In this stage, highway conditions including pavement distress, pot hole, road signs are automatically recognized by a AI based software CiAS (China's Highway information Auto-recognition System) as seen in Figure 4.1.6.5.
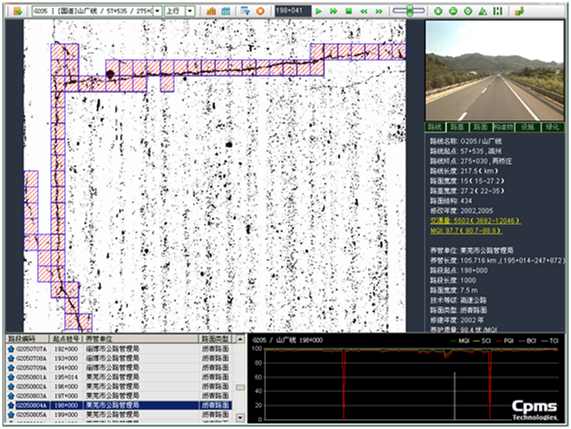
Figure 4.1.6.5: CiAS Distress Recognition
With the obtained highway condition data, highway condition evaluations can be conducted according to the Highway Performance Assessment Standard (MOT PRC, 2007), and further maintenance analysis can be performed by using the CRMS system (China's Road asset Management System), including performance prediction, road user cost estimation, maintenance needs analysis, budget assignment, project optimization, planning and scheduling as shown in Figure 4.1.6.6.
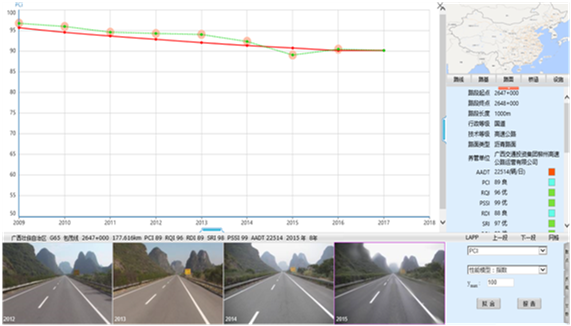
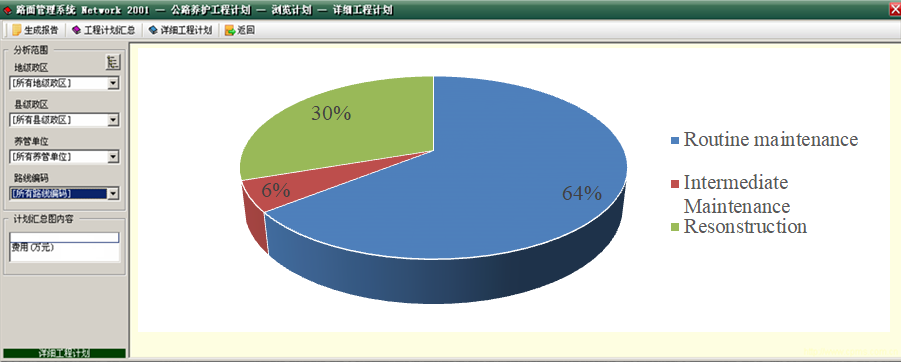
Figure 4.1.6.6: CPMS Maintenance Analysis
Planning, Scheduling and Presentation
The CRMS provides two sorts of platforms as shown in Figure 4.1.6.7 (PC Platform) and Figure 4.1.6.8 (Mobile phone platform). The two platforms enable the Highway Bureaus to conduct and present their highway network managing plans and maintenance schedules and mapping the results on the platforms, that automatically likes the visual information (maps, pavement images, front view images) with all other information such as inventory, maintenance history, current conditions, future performance and analysis results.
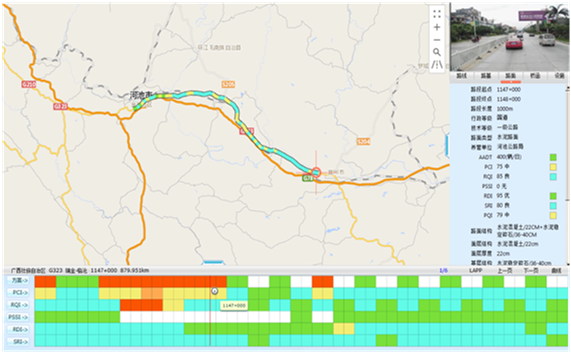
Figure 4.1.6.7: PC based CRMS
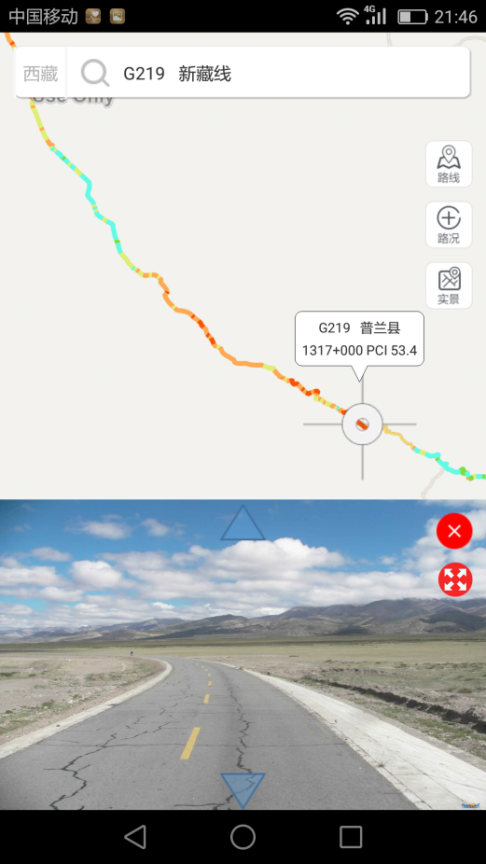
Figure 4.1.6.8: Mobile phone based CRMS
The annual based asset management conducted in Jiangsu Province has significantly changed the traditional manner of highway asset management. With the modern technologies, the Jiangsu Provincial Highway Bureau (and its district level Highway Bureaus) is able to manage their highway asset with a more cost-effective way, through the procedure of data collection, distress auto-recognition, whole life cycle cost-based maintenance analysis, and planning and scheduling.
Ministry of Transport, PRC.2017. Annual report of national highway maintenance statistics. Beijing.
L, Gao and X, Zhang. 2017. Construction of scientific decision-making system for trunk highway in Jiangsu Province. Maintenance Engineering (145) PP. 44-48.
Ministry of Transport, PRC. 2007. Highway Performance Assessment Standards. China Communications Press. Beijing.