
Asset Management Manual
A guide for practitioners!

Asset Management Manual
A guide for practitioners!
ALFRED WENINGER-VYCUDIL, PMS-Consult – Deighton Europe, Austria
The Austrian Pavement Management System is used for a network-wide objective maintenance planning process in consideration of different aspects and demands on different decision levels (project-level, network-level, policy-level). At the moment, it is applied on the whole Federal road network (motorways and expressways) with a total length of more than 2,200 km as well as on the State road network in 7 of 9 Austrian states (Vorarlberg, Tyrol, Salzburg, Styria, Upper Austria, Lower Austria and Burgenland). Furthermore, a similar approach is being used to assess community road pavements and pavements on rural roads in 3 Austrian states.
The system employed for systematic pavement maintenance planning is based on life-cycle cost analysis (LCCA) that provides a framework for decision-making for maintenance measures in order to optimize efficiency in terms of the use of the resources available or in terms of pavement condition. The procedure employs cost-benefit analyses as well as a heuristic optimization process to identify the optimum maintenance treatment strategy in a given set of conditions.
OBJECTIVES
One of the key tasks throughout the decision-making process is the highlighting of needs for maintenance budget for the different assets. This output allows the road administration authorities to clearly show the policy makers the long-term development of the condition distribution of the pavement for different budgets or level of service and also the consequences of reductions in road maintenance funding. The results of the life-cycle analysis include:
The forecast of future condition using life-cycle analysis is the most efficient way to manage pavements and offers different opportunities for the road administration. The analysis enables the road administration to assess different options in managing their pavements. The assessment of different maintenance treatment strategies on a section level is a comprehensive basis for the definition of the short- to medium-term pavement construction programs. Long-term results allow budget, maintenance and rehabilitation planning and optimization. Phases with high investments can be detected on an early stage and specific investment programs can be prepared in advance.
Advanced systems like the Austrian PMS seek to assess the need for maintenance measures and maintenance funding over a specified period under study or observation on the basis of predictions of pavement performance. The Austrian PMS employs deterministic performance functions for the prediction of pavement performance. These models were derived directly from the data available in the context of different research projects funded by the ASFINAG (motorways and expressways) and the Federal Ministry of Transport, Innovation and Technology (BMVIT) for the state roads.
In the context of PMS analysis, different maintenance relevant data are included as follows:
Since, as a rule, each performance indicator (characteristic) represents only one aspect or one property of the road pavement, the individual dimensional values (technical parameters) obtained for the various characteristics first have to be standardized as dimensionless indices, then aggregated into sub-indices by applying weighting and combination rules, and finally aggregated into an overall index.
For transforming dimensional values, standardization functions (normalization) have been defined which enable an assessment of the damage or defect as a function of the importance of the road section (motorway, expressway, state road). The dimensionless values thus obtained, are aggregated by applying weighting and combination rules to yield a comfort and safety index (CSI) expressing riding safety and riding comfort and into a structural index (SI) which represents the structural capacity of the pavement. The total condition index (TCI) resulting from the sub-indexes can be usedfor calculating the benefit of a maintenance strategy as well as for defining the target function as part of the optimization process.
The result of an analysis is a proposal for an optimum maintenance treatment strategy for each road section analyzed (as a function of the conditions defined), which can be used for further evaluation at project level. By aggregating section-based results, one can also assess developments in terms of cost and pavement conditions across the entire network level and, finally, determine the optimum maintenance requirements. The following two figures show an example of the analysis, where Figure 2.4.11.2 represents a pavement condition distribution and Figure 2.4.11.3 shows the development of the maintenance backlog for different subnetworks in form of a comparison.
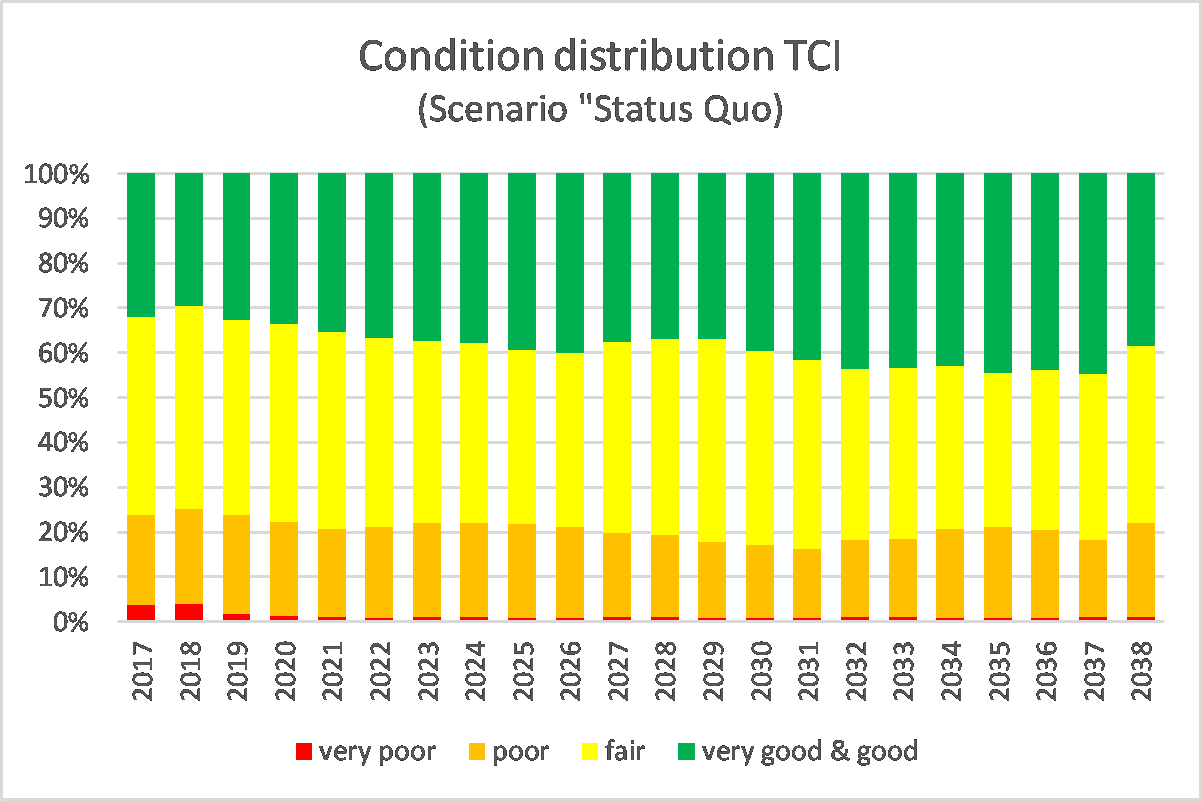
Figure 2.4.11.2: Condition distribution of Total Condition Index (TCI) for Scenario “Status Quo”
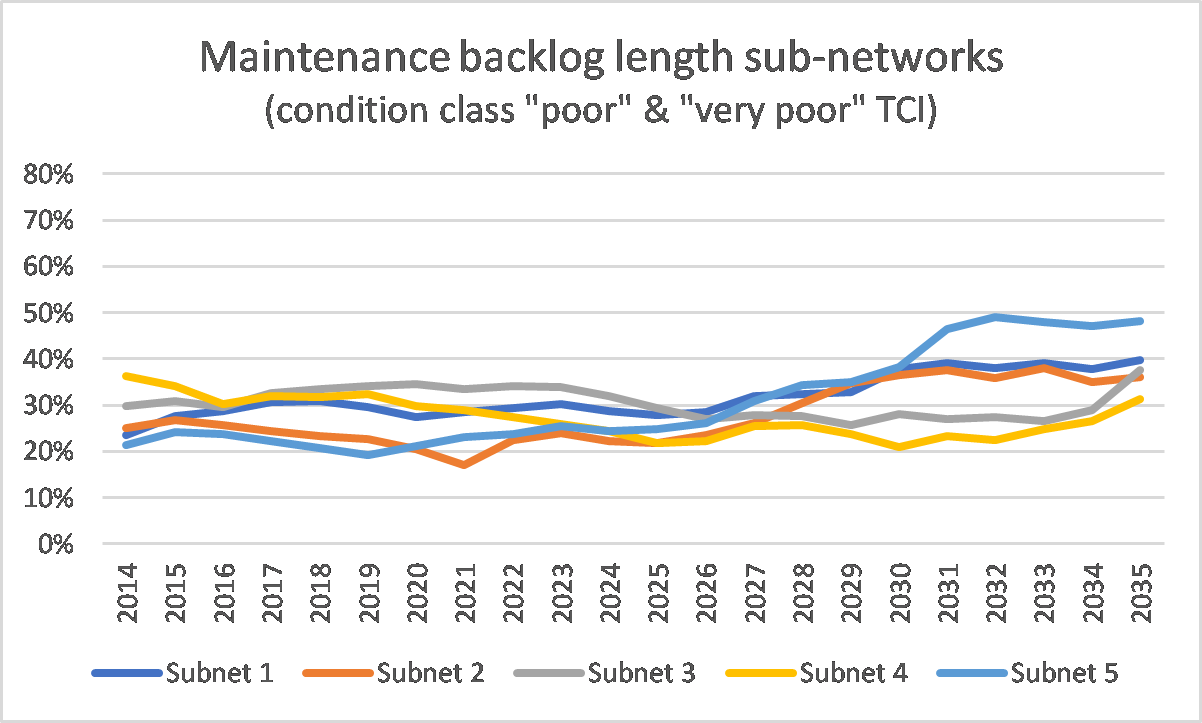
Figure 2.4.11.3: Maintenance backlog length Total Condition Index (TCI) for different subnetworks
The practical application of the PMS relies on a computer-assisted asset management tool of Canadian origin (dTIMS© - Deighton Total Infrastructure Management System), which employs a deterministic optimization model for selecting the most effective maintenance treatment strategy in the context of life-cycle-cost analysis. In choosing the system, the decisive factor had been that algorithms and models can be modified and defined by the user as necessary to enable effective control or adaptation to the road network and general framework conditions.
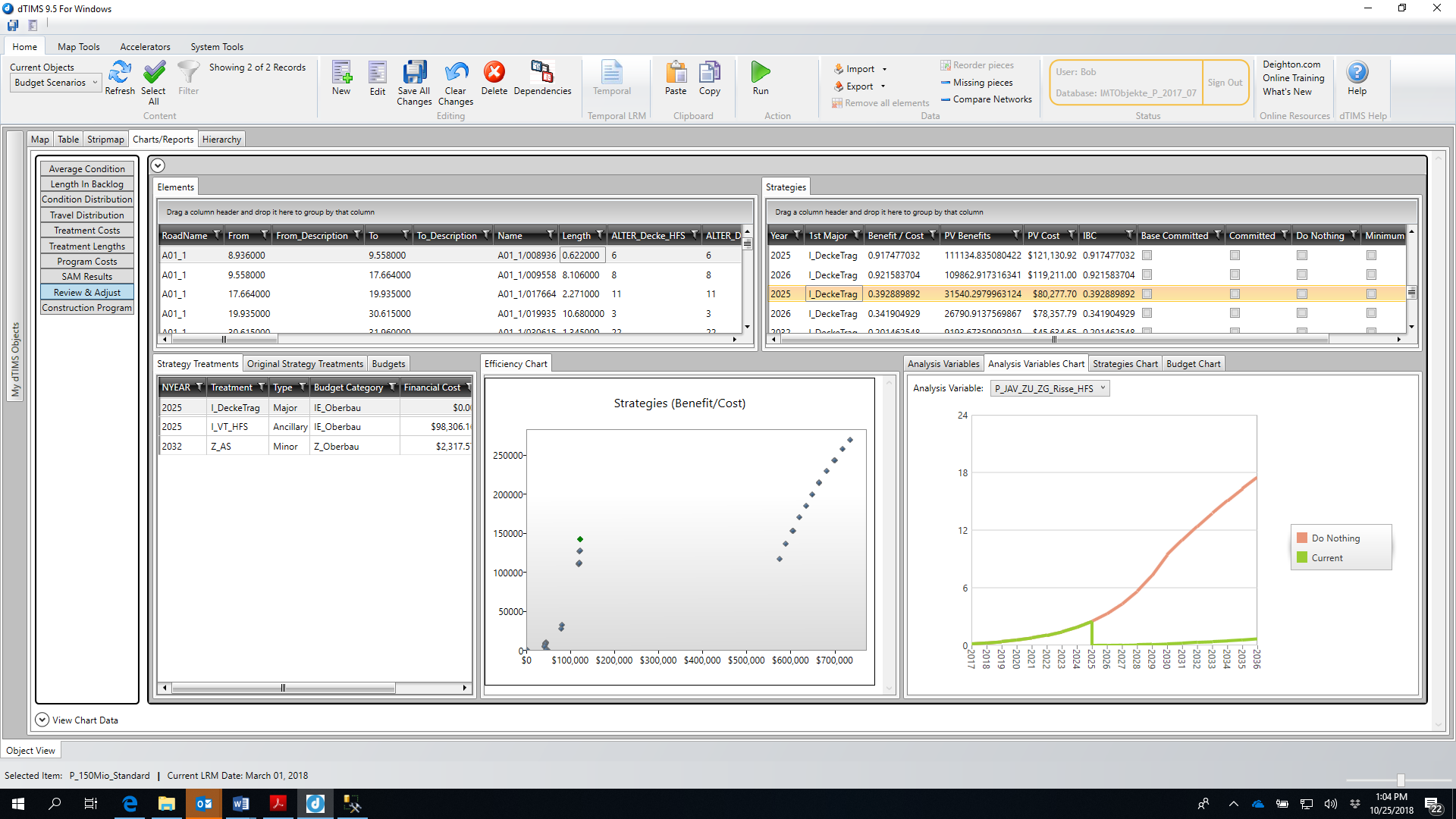
Figure 2.4.11.4: Screenshot dTIMS – Austrian PMS-Application – LCC-Window
Pavement management systems using life-cycle cost analysis have become a standard in many countries around the world over the last 30 years. Beside having an objective instrument for underlining the need for maintenance investments, the solution enables the road administration to model future condition and investment needs for individual roadway segments and for the overall network. Austria is a good example how life-cycle cost analysis has and will be used as technical and strategic planning tool on the different road networks.