

Structured information management assists the asset manager to optimize the overall asset management goals. The ISO 19650 standards, by positioning BIM in a direct environment of Asset Management and by showing the mutual relations, have given considerable impetus and incentive for the adoption of asset management systems by the road infrastructure owner and operator. Figure 4.3.6.1 shows the relationship between the information generated through the asset management system and BIM, how they are generated, and how they are connected (Miskimmin).
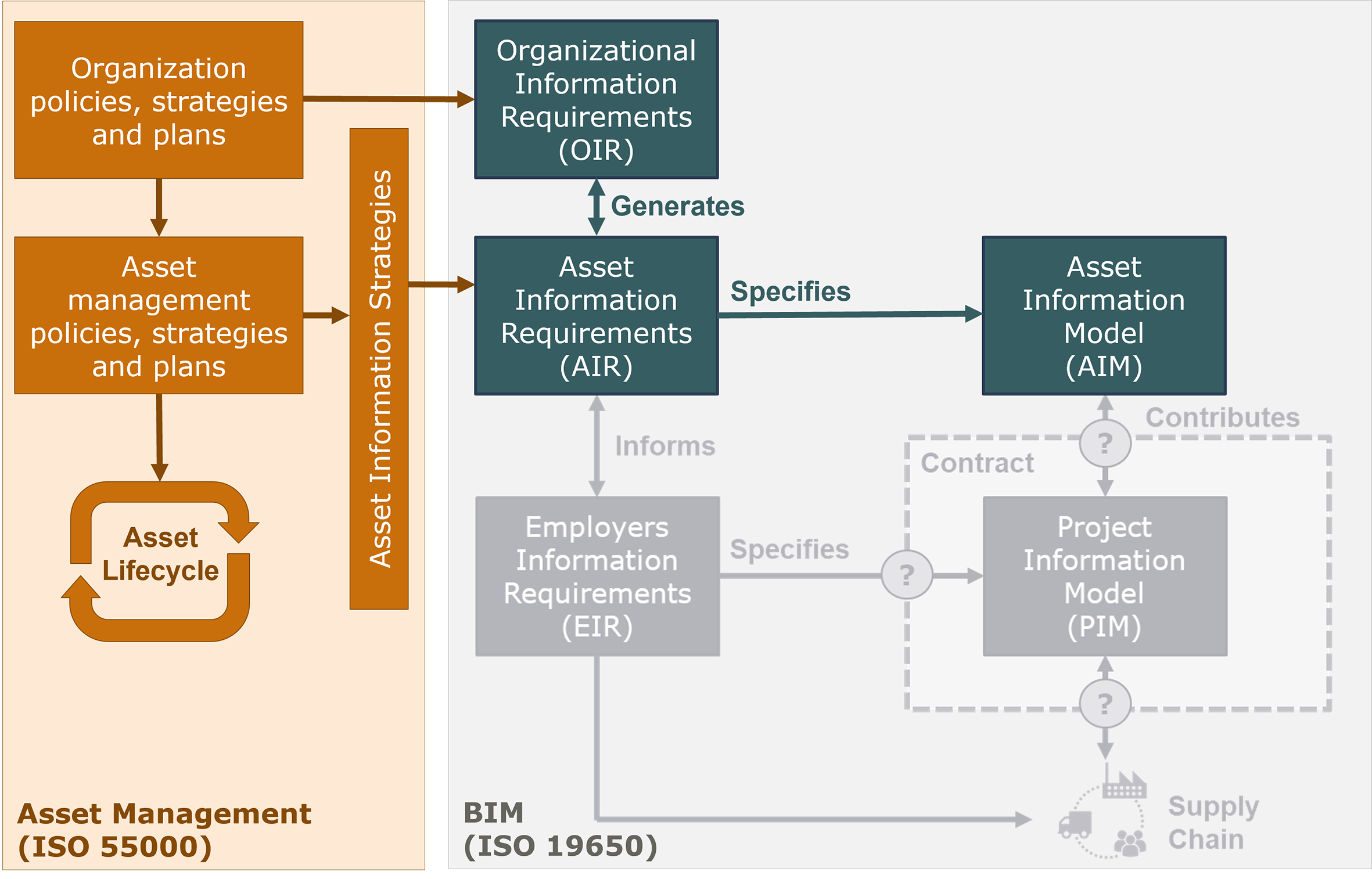
Figure 4.3.6.1 Relationship between Information generated in Asset Management and BIM (on the basis of Miskimmin)
It is certain that BIM will continue to be one of the most dynamically developing disciplines. This is definitely true for the technical BIM-solutions and hopefully also for the management solutions in the organizational environment of Asset Management.
BIM for all phases of lifecycle
Although the BIM methodology requires that the entire lifecycle of a given asset must be considered, the overwhelming majority of practical applications of BIM are still limited to design and construction. While for most building construction objects such an approach may be justified and rational, the asset manager of horizontal infrastructure, such roads, when planning the new construction, upgrading or renewal of a road, usually has to consider the subsequent actions within a road section, i.e. the repair or renewal actions resulting from the scenario provided by the Pavement Management System. Thus, this 4th dimension of BIM, that is time, is of particular importance for road infrastructure and should be extended to the whole life of the road section.
BIM for entire Asset Portfolio
The specific nature of transportation investments puts an additional, very important requirement on BIM. The coordination of construction plans by managers of different infrastructure systems responsible for the entire infrastructure portfolio is necessary, but this is a major challenge due to the frequent lack of organizational structures dedicated to the coordination of such tasks. The need to consider the entire infrastructure portfolio does not mean that every BIM project is burdened with further constraints and restrictions. However, the infrastructure manager must be aware of these realities and take them into account both in the formulation of the Asset Management Strategy by itself and in the requirements for individual BIM projects.
Continuing education of BIM professionals
One of the challenges in implementing BIM in the road sector is overcoming barriers and the lack of awareness among managers in road administrations regarding the benefits that targeted application of the discipline's methods will bring to them. This is confirmed by numerous surveys and polls. Considering BIM only as a tool for 3D modeling that supports the designer makes it very difficult to promote BIM as a management method.
Therefore, educational activities to disseminate and promote BIM and to raise awareness of its importance in the context of information management will play an increasingly important role. The broader the knowledge of the possibilities of BIM applications according to ISO 19650 among asset managers, the greater likelihood that managers will demand the development and implementation of BIM procedures.
Over time, two BIM streams have emerged. One stream is oriented towards optimizing the planning and construction phase of individual projects. The principle of this stream is: first build digitally and only then build for real. The addressees are the planning and construction companies. This BIM stream is mostly associated with 3D modeling.
The second BIM stream is oriented towards the entire road network and the primary addressees are the owners and operators of the infrastructure. The mission is to support broad digitalization in order to optimize the main objectives of the infrastructure owner. So, the message is addressed to the owner and operator and reads: keep control over your network data to optimize your goals. The main reference source of this second BIM stream is ISO 19650.
The appropriate implementation of BIM by the operator for all construction activities can lead to a breakthrough in digitalization in the road construction sector. The implementation of BIM in the road administration of the operators will also contribute to a better use of the information already managed in road databases. The simple existence of information and its availability is not enough. Only the transformation of information into knowledge, by making it available to the stakeholders involved and by a targeted exchange between all parties involved in engineering activities and decision-making processes, gives this information a real, tangible value. The result will be an increase in the quality and efficiency of the work, an increase in the agency’s rank and reputation, and an increase in the satisfaction of its employees.